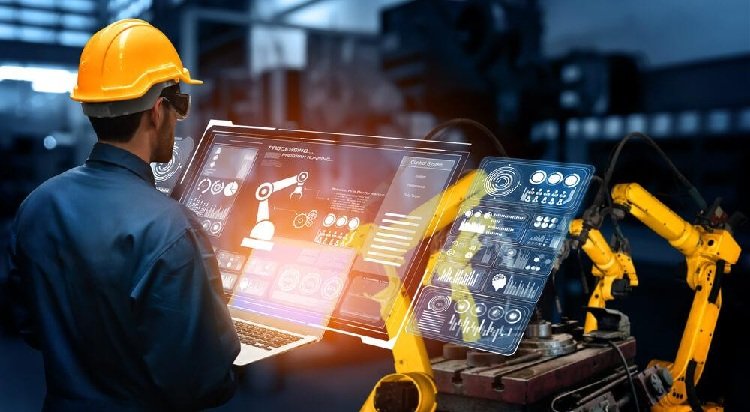
Industrial automation has been transforming manufacturing and production for decades, and its evolution shows no signs of slowing down. As technology advances, industries worldwide are embracing automation to boost efficiency, reduce costs, and improve product quality. Looking ahead, several key trends are shaping the future of industrial automation, revolutionizing how factories and plants operate. In this blog post, we’ll explore the most important trends that are driving the next wave of industrial innovation.
1. Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are no longer futuristic concepts—they are rapidly becoming essential tools in industrial automation. AI-powered systems can analyze massive amounts of data from sensors and machinery in real time, enabling predictive maintenance, process optimization, and quality control.
Machine learning algorithms help identify patterns and anomalies, predicting equipment failures before they happen. This reduces downtime, saving companies millions in repair costs and lost productivity. Furthermore, AI enhances decision-making by providing actionable insights that humans alone might overlook, making factories smarter and more adaptive.
2. The Rise of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) connects machines, sensors, and control systems over the internet, enabling seamless data exchange and communication. IIoT networks allow real-time monitoring of production lines, remote control of machinery, and faster response times to problems.
With IIoT, manufacturers gain unprecedented visibility into their operations, facilitating better resource management and faster troubleshooting. This connectivity also supports automation at scale, where multiple systems work together autonomously to optimize the entire production ecosystem.
3. Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Unlike traditional industrial robots that operate in isolation, collaborative robots—or cobots—are designed to work alongside human workers safely. Cobots assist with repetitive, precise, or dangerous tasks while allowing humans to focus on complex, strategic work.
The use of cobots is growing rapidly due to their flexibility, ease of programming, and affordability. They can be deployed quickly on production floors without extensive retooling. As a result, small and medium-sized enterprises can now leverage automation to improve productivity without heavy upfront investments.
4. Edge Computing for Faster Processing
Edge computing refers to processing data near the source of generation, such as on factory floors or devices themselves, rather than relying solely on centralized cloud servers. In industrial automation, this reduces latency—the delay in data transmission—enabling faster real-time responses.
For critical applications like quality control and safety monitoring, milliseconds matter. Edge computing allows systems to make instant decisions without waiting for cloud analysis. This improves operational reliability and enables advanced automation capabilities that require quick reflexes.
5. Advanced Human-Machine Interfaces (HMI)
As automation becomes more sophisticated, user interfaces have evolved beyond simple buttons and screens. Advanced HMIs, including touchscreens, augmented reality (AR), and voice controls, are making it easier for operators to interact with machines.
AR, for example, can overlay digital information on physical equipment, guiding workers through maintenance or troubleshooting tasks step-by-step. Such intuitive interfaces reduce training time, lower errors, and enhance overall productivity on the factory floor.
6. Sustainable and Energy-Efficient Automation
Sustainability is becoming a major focus in industrial automation. Companies are seeking automation solutions that not only improve efficiency but also reduce environmental impact.
Automation systems now include energy monitoring and management features that optimize power usage. Smart controls can shut down idle machines or adjust operations based on energy demand, helping factories lower their carbon footprints. The integration of renewable energy sources with automated systems is another emerging trend.
7. Increased Cybersecurity Measures
With growing connectivity through IIoT and cloud platforms, industrial automation faces heightened cybersecurity risks. Protecting critical infrastructure from cyberattacks is vital to prevent costly disruptions or safety hazards.
The future of industrial automation includes stronger cybersecurity protocols—such as encryption, network segmentation, and continuous threat monitoring—to safeguard data and operations. Manufacturers are investing in secure automation technologies to build resilient, trusted systems.
8. Customizable and Scalable Automation Solutions
One-size-fits-all automation is becoming a thing of the past. Today, manufacturers demand flexible, modular automation systems that can be customized to specific needs and scaled as production grows or changes.
Advances in software, robotics, and cloud platforms enable companies to tailor automation setups and easily upgrade or reconfigure them. This agility allows businesses to respond faster to market demands and reduces long-term costs.
In Conclusion
The future of industry is grounded in leveraging cutting-edge automation technologies to transform manufacturing processes. Key innovations like AI, IIoT, collaborative robots, edge computing, and sustainable automation are driving a new era where factories become smarter, safer, and more efficient. Additionally, the adoption of high flux density cores in industrial equipment is enhancing performance by enabling more compact, energy-efficient, and powerful electrical systems. As these technologies evolve and become more widely accessible, companies of all sizes stand to gain from accelerated production cycles, superior product quality, and reduced operational costs.
Keeping abreast of these developments is crucial for manufacturers and industry leaders aiming to navigate the upcoming technological revolution. Embracing advanced automation and innovations such as High Flux Density Core utilization isn’t merely a competitive edge—it’s a necessity for thriving in the rapidly evolving, technology-driven landscape of tomorrow’s industry.